The Microscope’s Turret: A Gateway to Magnification?
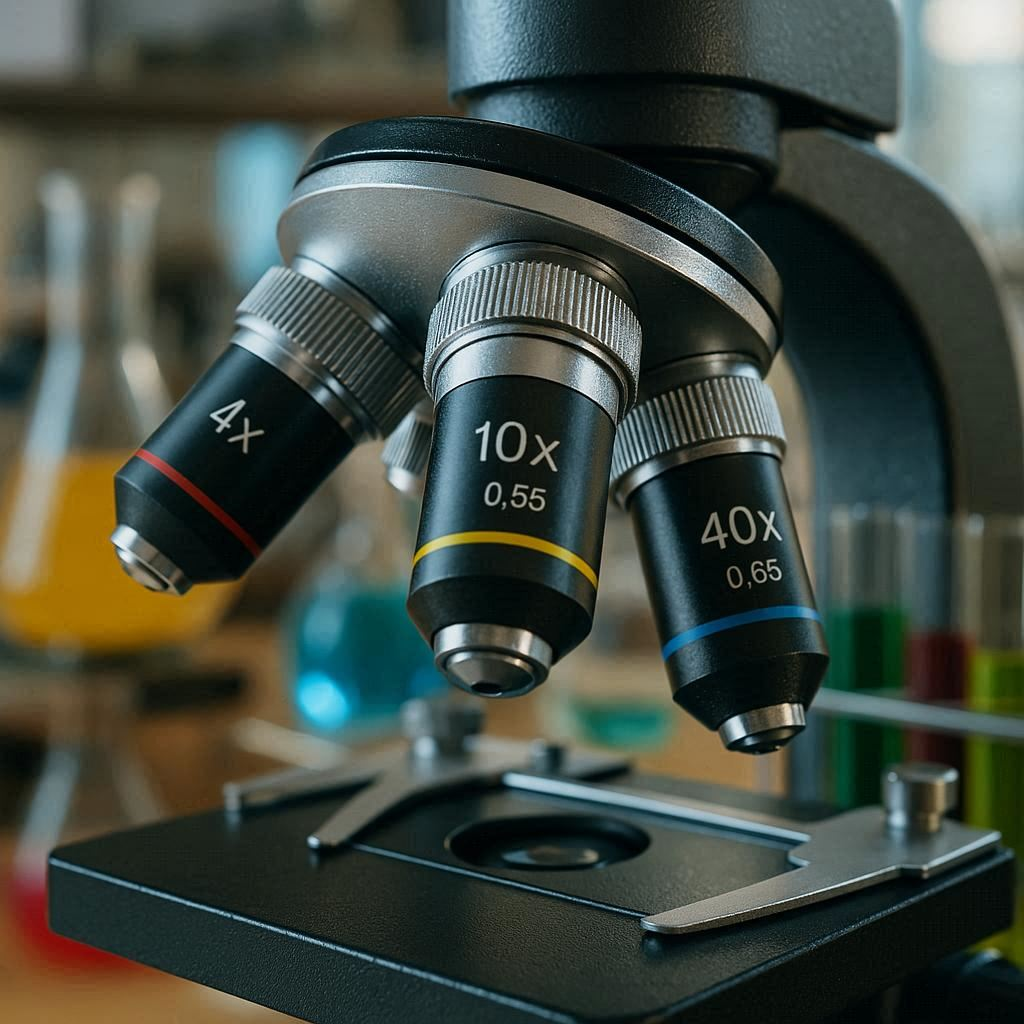
The component that holds two or more objective lenses and can be rotated to change power in a microscope is the revolving nosepiece, also commonly known as the objective turret. This crucial piece of microscope hardware is the central hub for the objective lenses, which are the primary magnifying elements in a compound light microscope. Located at the lower end of the microscope’s body tube, just above the stage, the rotating turret is designed to securely hold multiple parfocal objectives, each with a different magnification power, such as 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. The ability to smoothly rotate this lens holder allows the user to quickly and easily switch between these different magnification levels without having to manually screw and unscrew each individual objective lens. This seamless transition is vital for efficient microscopy work, enabling the user to locate a specimen with a low power, scanning objective and then progressively rotate to higher power objectives for more detailed observation, all while maintaining relative focus, a feature known as parfocality.
The design and precision of the revolving nosepiece are critical for maintaining optical accuracy and image quality. A high quality, sturdy nosepiece mechanism ensures that each clicked position aligns the corresponding microscope objective perfectly with the microscope’s optical path. This precise alignment is necessary to keep the specimen in the center of the field of view and to guarantee that the image remains sharp and free from aberrations. The objective changer operates on a precise clicking mechanism, where each lens snaps securely into place, ensuring stability during observation and preventing any wobble that could blur the image. This robust construction protects the expensive and delicate objective lenses from damage. The entire lens rotating mechanism is a testament to mechanical and optical engineering, integrating seamlessly with the coarse and fine focus adjustments to provide a user friendly experience. Without this simple yet ingenious rotating component, the process of changing magnifications would be cumbersome and time consuming, significantly hindering scientific investigation and discovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is another name for the revolving nosepiece?
Answer: It is also commonly called the objective turret or simply the turret.
Question: Why is it important that the nosepiece rotates smoothly?
Answer: Smooth rotation allows for quick magnification changes and prevents jolts that could damage the lenses or move the specimen.
Question: What does “parfocal” mean in relation to the nosepiece?
Answer: Parfocal means that when you switch between objectives on the same nosepiece, the specimen remains in relative focus, requiring only minor fine-focus adjustments.
Question: How many objective lenses can a typical nosepiece hold?
Answer: Most standard microscopes have a nosepiece that holds three, four, or five objective lenses.
Question: Can the nosepiece be replaced or upgraded?
Answer: Yes, but it must be compatible with the microscope model to ensure proper optical alignment and mechanical fit.
Question: What should you be careful of when rotating the nosepiece?
Answer: Always grip the nosepiece itself, not the objective lenses, to rotate it, and do so gently to avoid misalignment or damage.
Question: Is the revolving nosepiece found on all types of microscopes?
Answer: It is a standard feature on compound light microscopes but is not typically found on stereoscopes or high-end electron microscopes.
Question: What is the lowest power objective usually mounted on the nosepiece?
Answer: The lowest power is typically the 4x scanning objective, used for initially locating the specimen.
Question: How does the nosepiece contribute to the total magnification?
Answer: The total magnification is calculated by multiplying the power of the objective lens on the nosepiece by the power of the eyepiece.
Question: What maintenance does the nosepiece require?
Answer: It should be kept clean and dust-free, and its movement should be checked periodically to ensure it clicks securely into place.
Keywords: revolving nosepiece, objective turret, microscope objective lenses, magnification power, rotating turret, lens holder, nosepiece mechanism, objective changer, lens rotating mechanism, parfocal objectives, compound microscope parts, optical path, mechanical stage
Tags: #MicroscopeParts #RevolvingNosepiece #ObjectiveTurret #Microscopy #Magnification #ScientificInstrument #Optics #BiologyLab #MicroscopeObjectives #ScienceEducation